The Robot Automation Program (RAP) is an application which allows factory technicians to create and edit the weld placement programs for various robots on the assembly line. Both transactions maintain the Weld Specification and Robot logical files.
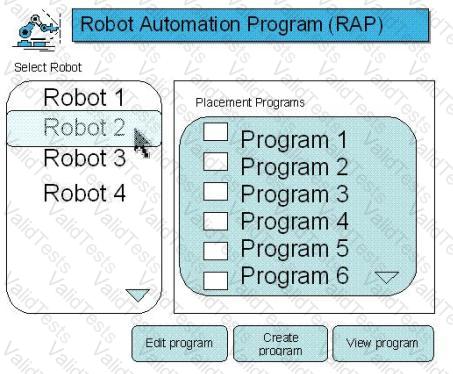
The use may select and view reboot details:
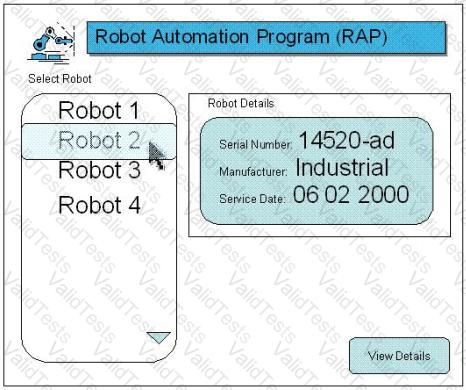
The user may print individual welding program details:

From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the transactional functions for the RAP application. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Functions does not apply.
Identify the functions used:
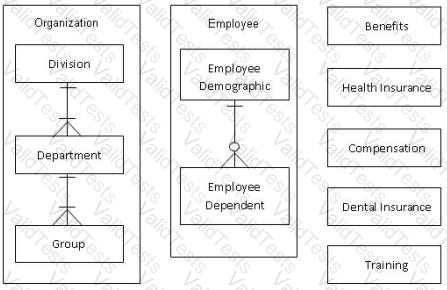
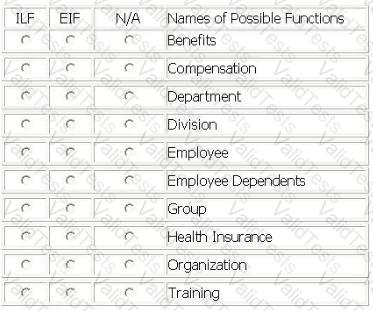
The Organization consists of three levels of organizational hierarchy. There are one or more Groups to a Department and one or more Departments to a Division. When a Division is deleted all associated Departments and Groups are also deleted. Organization data (including all three parts) is maintained by the Payroll application.
All the remaining tables are maintained by the HR application.
All the remaining data is maintained by the HR application.
The HR application stores information on the employee in the Employee logical file. Employee dependent information about the spouse and children of the employee are stored on the Employee Dependent table.
Health insurance plan, dental insurance plan, life insurance, and accident insurance data is stored in the Benefits logical file.
Pay rate, bonus percentage, vacation accrual rate, vacation balance, and pension accrual rate are stored on the Compensation logical file.
Training classes attended and scheduled are stored in the Training logical file.
The health insurance table contains the code and description for all Health Insurance plans offered to the employees for health coverage.
The dental insurance table contains the code and description for all Dental Insurance plans offered to the employee for dental coverage
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the data functions for the HR application. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Function does not apply.
Identify the data functions used:
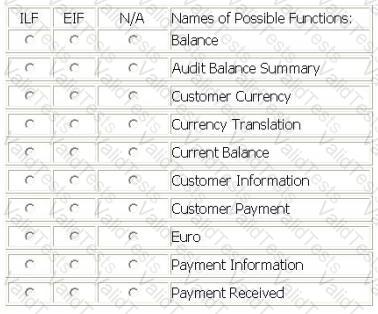
Several data functions are described in the scenario for the Accounts Receivable fAFO application:
From the main menu, the user selects the receive payment option.
The receive payment option opens a screen which allows the user to enter payment information in the Payment Information logical file. The receive payment option updates the Customer Payment logical file to store the outstanding balance due. If there is no existing outstanding balance, the current balance is added to the Customer Payment logical file.
The Currency Translation file is imported daily from the Banking Application and updates the AR application's Customer Currency logical file. The Customer Currency logical file is used by the AR application to translate the currency from the customer's local currency to the Euro. The user also maintains the country code and full country name in the Customer Currency logical file.
The user maintains the customer name, address and account number in the Customer Information file in the AR application.
From the main menu, the user selects the balance review option.
The balance review option accesses the Customer Payment logical file. The balance summary option allows the user to create a balance summary report by customer. This report is viewable on the screen, can be emailed to a user, downloaded to a spreadsheet, and printed to hardcopy. For audit purposes, every balance summary report is saved to the Audit Balance Summary logical file.
The balance detail option accesses the Customer Information, Customer Payment and Customer Currency logical files. A printed report is created that contains a list of all customers with balance changes in the current month. The balance is shown in both customer local currency and the Euro. The report also includes the customer address with country name after translating the country code using the Customer Currency logical file.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the data functions for the AR application. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Function does not apply.
Identify the functions used:
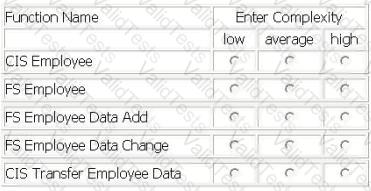
CORPORATE INFORMATION SYSTEM (CIS) - EMPLOYEE DATA TRANSFER
From the CIS main menu, the CIS user selects the Transfer Employee Data option.
The Transfer Employee Data option creates a transaction file of CIS Employee logical file records that have a status flag equal to Add or Change. Each record in the transaction file contains employee badge number, first name, last name, phone number, facility, supervisor badge number, organization, job code, and status flag.
The CIS transaction file is written to the Financial System (FS) server's temporary file work area. This data transfer is a user requirement for both applications.
From the FS main menu, the FS user selects the Load Employee Data option.
The Load Employee Data option accesses the CIS transaction file from the FS server's temporary file work area. The Load Employee Data option processes the input records according to the status flag, initiating different processing logic for Add and Change. The Load Employee Data option loads all attributes from each record to the FS, except the status flag.
As part of the same elementary process, when an employee is being Added or Changed to the FS Employee logical file it also saves the employee's pay grade code, retrieved from the Payroll System.
Both applications have a requirement to access a version of the Employee logical file.
Determine the complexity for the functions listed.
Select the complexity for each function:
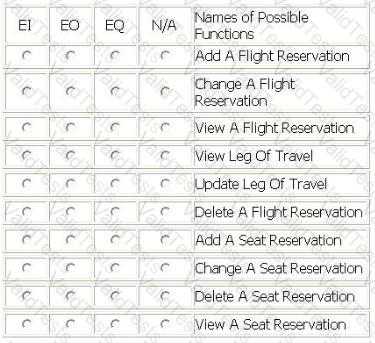
A Flight Reservation application has the ability to make a reservation and reserve a seat.
A passenger calls to make a reservation. The booking agent adds the information into the Flight Reservation logical file.
At a later time the passenger can make a change to the reservation through the booking agent.
The booking agent views the flight reservation record before changing it.
The booking agent can also reserve a seat for the passenger for each leg of his travel, but cannot change or delete the seat reservation once made. Seat reservations are stored in the Seat Reservation logical file.
The booking agent can view the seat reservation record.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the transactional functions for the Flight Reservation application. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Functions does not apply.
Identify the functions used:
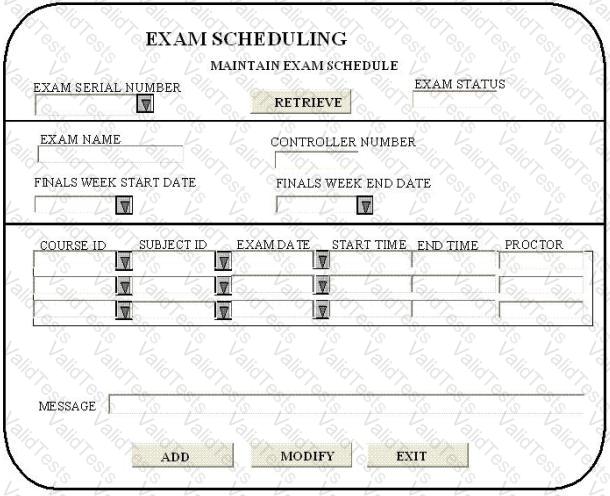
EXAM SCHEDULING SYSTEM (ESS) - EXAM SCHEDULING FUNCTIONS
The controller uses the Maintain Exam Schedule screen to schedule exams for various courses and subjects.
The exam serial number from the University Master logical file is entered in the screen. On pressing the Retrieve key, the exam name, controller number, finals week start date and finals week end date efe displayed from the University Master logical file. In addition, exam status, course id, subject id, exam date, start time, end time, proctor and message are displayed from Schedule Information logical file.
The Add or Modify options allow addition/update to the course id, subject id, exam start date, start time, end time, proctor and message using the exam serial number as the key field. The data in the add/update mode gets saved in the Schedule Information logical file with the 'pending approval' in the exam status, no other data is stored.
Course id, subject id and exam date pick lists provide data from static tables.
The exam dates should be within the finals week start and end dates
Determine the complexity for functions listed:
Select the complexity for each function:
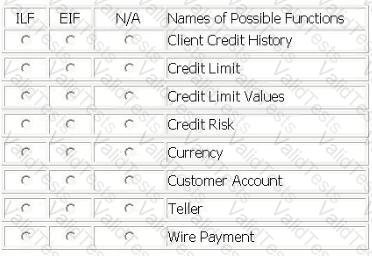
A baseline count is to be conducted for the Payment Information Application (PIA).
Client Credit History logical file is made available to the teller while processing a customer's wire payment. The Client Credit History logical file is retrieved from the Credit Master Application (CMA).
PIA also receives an end-of-day import file of wire payments from the Foreign Banking (FB) application. PIA maintains all customer wire payments in the Wire Payment logical file. During the processing of the wire payments, the currency is converted from the customer's local currency to PIA's currency using the FB application Currency logical file.
The teller must review the client credit history, and then update the Credit Limit logical file in the PIA before processing the wire payment.
Tellers maintain the Customer Account logical file using the maintain customer account function within PIA.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the data functions for the PIA. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Function does not apply.
Identify the data functions used:
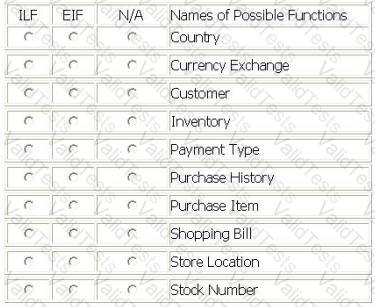
Several data functions are described in the scenario for the Internet Application (IA):
The user may query store locations where an order can be picked up. The Store Location logical file is updated in the IA as new locations open
The user may pay their internet shopping bill using the purchase item option. This option updates the Customer logical file with the date of purchase, the Inventory logical file with stock number and quantity, and Purchase History logical file with date, stock number, price and discounts applied.
Prior to the completion of the purchase item option the purchase amount is converted from US dollars into the user' s local currency. The currency conversion requires reference data from the Currency Exchange logical file, which Is maintained through the Financial application. The Currency Exchange file is updated daily. The payment code is used to determine how the payment will be made.
If this is the user's first purchase, customer Information is added to the Customer logical file. As part of adding customer information the Country file is referenced in order to store country code in the Customer logical file rather than country name.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the data functions for the IA. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Function does not apply.
Identify the data functions used:
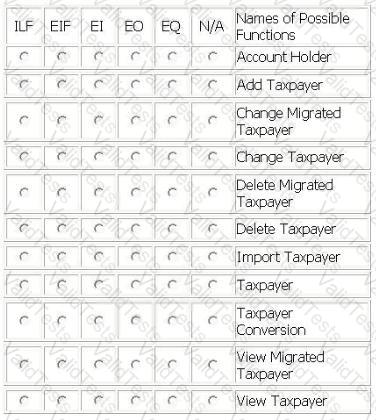
TAX APPLICATION
For the TAX application the user required the migration of existing taxpayer information (name, tax identification number, location name) to the TAX application. A conversion file with taxpayer data was created and imported into the Taxpayer logical file in the TAX application. The source of the data was the Account Holder logical file.
The user required the ability to Add, Change and Delete the taxpayer information in the Taxpayer logical file.
The user required the ability to View the taxpayer information prior to changing or deleting information.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the base functional components for the TAX application baseline. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Functions does not apply.
Identify the functions used:
The Procurement application user requires the ability to control how and when reports are printed. The following list shows the specific user requirements for generating reports:
Display a list of reports that are available to be printed.
The user selects a report to be printed. If report control information exists for the requested report, the report control is displayed from the Report Control logical file.
If report control information has not been specified for the requested report, the user may add the following report controls:
report id
sort sequence
printer port
whether or not to generate a microfiche copy
whether or not to generate a paper copy
If report control information exists for the requested report, the user may update or delete the report controls.
From the Names of Possible Functions listed identify the transactional functions for the Procurement application. Select N/A if a Name of Possible Function does not apply.
Identify the functions used:
